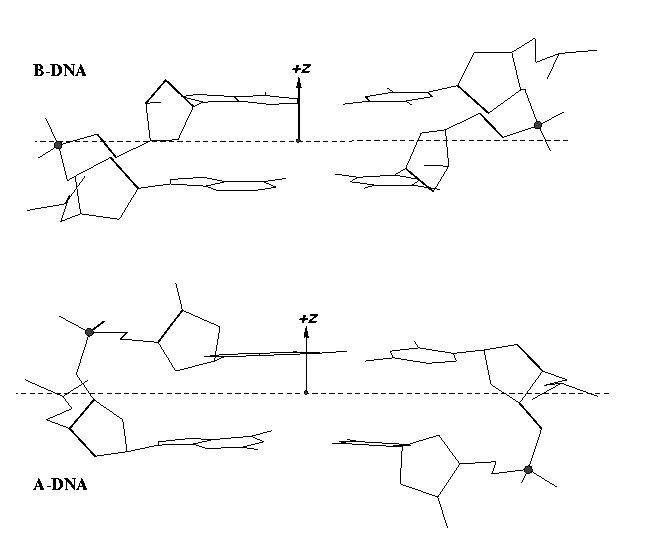
From early on, 3DNA calculates the Zp parameter to separate A- and B-DNA double helical steps. First introduced in the paper A-form conformational motifs in ligand-bound DNA structures (see figure below), Zp is the mean projection of the two phosphorus atoms onto the z-axis of the dimer ‘middle frame’. Zp is greater than 1.5 Å for A-DNA, and it is less than 0.5 Å for B-DNA. As noted in the 3DNA NAR paper, other parameters such as slide should also be examined to confirm conformational assignments based on Zp.
As of v2.1, 3DNA has introduced the single-stranded variant for the Zp parameter (ssZp) as a more robust substitute for the Richardson phosphorus-glycosidic bond distance parameter (Dp) to characterize sugar puckers. See post Sugar pucker correlates with phosphorus-base distance for more details. In 3DNA/DSSR, ssZp is defined as the z-coordinate of the 3′ phosphorus atom expressed in the standard reference frame of the preceding base; it is positive when phosphorus lies on the +z-axis side (base in anti conformation) and negative if phosphorus is on the –z-axis side (base in syn conformation). Note that by definition, Dp should always be positive.
As in the previous post, here I am using G175 and U176 of PDB entry 1jj2 (the large ribosomal subunit of Haloarcula marismortui) as examples to illustrate how the ssZp parameters are calculated. The GpU forms a dinucleotide platform, where the sugar of G175 adopts a C2′-endo conformation, and that of U176 C3′-endo. For verification, here is the PDB data file for fragment 1jj2-G175-U176-A177.pdb (note A177 is included for its phosphorus atom). Run the following 3DNA commands:
find_pair -s 1jj2-G175-U176-A177.pdb stdout frame_mol -1 ref_frames.dat 1jj2-G175-U176-A177.pdb ref-G175.pdb frame_mol -2 ref_frames.dat 1jj2-G175-U176-A177.pdb ref-U176.pdb
File ref-G175.pdb contains the following line:
ATOM 24 P U 0 176 -5.624 6.937 1.918 1.00 24.19 P
The z-coordinate of U176 (which is 3′ to G175) is 1.918, which is the ssZp for G175. It is less than 2.9 Å, corresponding to the C2′-endo sugar conformation of G175.
Similarly, file ref-U176.pdb contains the following line:
ATOM 44 P A 0 177 -3.841 6.592 4.377 1.00 25.91 P
So the ssZp for U176 is 4.377, which is greater than 2.9 Å, corresponding to the C3′-endo sugar conformation of U176.
To sum up, the double-stranded Zp as originally available from 3DNA can be used for discriminating A- and B-DNA double-helical steps: Zp > 1.5 Å for A-DNA, and Zp < 0.5 Å for B-DNA. The newly introduced single-stranded Zp is intended for characterizing sugar puckers: Zp > 2.9 Å for C3′-endo, and Zp < 2.9 Å for C2′-endo. Since A-DNA has predominately C3′-endo sugar conformation and B-DNA has C2′-endo sugar, the ssZp parameter would be helpful in classifying a dinucleotide into A- or B-like conformation. A survey of ssZp in well-defined A- and B-DNA structures (as performed for double-stranded Zp) should prove useful.
Realizing the naming confusions of double-stranded Zp vs single-stranded Zp, I am considering to rename single-stranded Zp as ssZp in future releases of 3DNA and DSSR. Do you have any comments or suggestions? Please let me know by leaving a comment!